When you’re ordering carbide tools or carbide tips for industrial use, one of the most important decisions you’ll make is choosing the correct carbide grade. The right grade ensures optimal performance, efficiency, and durability, ultimately affecting your bottom line and productivity.
However, with so many grades available, understanding how to compare them can be a challenge, especially if you’re new to the world of carbide tips.
In this article, we’ll explore what carbide grades are, why they matter, and how to effectively compare them when ordering cutting tools for your next industrial project.
Whether you’re involved in manufacturing, metalworking, or other precision industries, this guide will help you make more informed choices when selecting carbide tools.
What Are Carbide Grades?
Carbide grades refer to the specific composition and material properties of carbide tips and carbide tools used for cutting and machining applications.
These grades are determined by the combination of materials used in the carbide, such as tungsten carbide and cobalt, as well as the processing methods that affect the tool’s characteristics.
The grade of carbide affects several key factors:
- Hardness: The ability of the carbide to resist deformation under pressure.
- Wear Resistance: How well the carbide can withstand the friction and abrasion encountered in industrial applications.
- Toughness: The ability of the carbide to resist breaking or cracking under stress.
- Heat Resistance: How well the carbide can handle high temperatures, especially in high-speed cutting processes.
Why Is Choosing the Right Carbide Grade Important?
The correct carbide grade is essential to ensuring that cutting tools perform effectively and last as long as possible in industrial environments. Using the wrong carbide grade can lead to premature wear, poor cutting performance, or even tool failure. Here’s how the grade can impact your operations:
- Tool Longevity: Higher-grade carbide tips offer better wear resistance, meaning they last longer and require fewer replacements.
- Performance: The right carbide grade ensures that your cutting tool maintains sharpness and delivers precision cuts consistently.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Choosing the correct grade helps you avoid unnecessary downtime and replacement costs, contributing to greater overall efficiency.
- Safety: Properly selected carbide grades reduce the risk of tool failure, which can lead to safety issues in the workplace.
How to Compare Carbide Grades
Now that we understand why carbide grades are important, let’s look at the key factors to consider when comparing grades for your carbide tools.
1. Hardness vs. Toughness: Finding the Right Balance
One of the primary factors in selecting a carbide grade is balancing hardness and toughness. Carbide tools need to be hard enough to cut through tough materials, but they also need to be tough enough to withstand the stresses of cutting and prevent cracking.
- Hardness: A harder carbide grade will maintain sharpness for longer and be more resistant to wear, making it suitable for cutting hard materials like steel or ceramics.
- Toughness: A tougher grade of carbide is better for applications where the tool will face heavy impact or shock loads, such as in rough machining operations or in applications with variable cutting forces.
Choosing a grade that offers the right balance between these two properties is crucial. For example, fine-grain carbide grades are harder but more brittle, while coarse-grain carbide grades are tougher but less wear-resistant.
2. Consider the Material Being Cut
The material you are cutting plays a significant role in selecting the right carbide grade. Different materials demand different tool properties, and choosing a grade that matches the material is key to achieving the best results.
- Soft Materials: For cutting soft materials like aluminum or plastics, you may not need a very hard carbide grade. A tougher grade with moderate hardness will suffice for these materials.
- Hard Materials: When cutting hard materials such as steel, titanium, or high-temperature alloys, a harder carbide grade with high wear resistance is essential to maintain sharpness and prevent rapid degradation of the tool.
- Abrasive Materials: If you’re cutting materials like cast iron or composites, which are highly abrasive, a carbide grade with high wear resistance is required to prevent the tool from wearing out too quickly.
3. Workpiece Size and Cutting Conditions
The size of the workpiece and the cutting conditions should also be considered when selecting the carbide grade. In high-speed machining or heavy-duty cutting scenarios, you may need a carbide grade with high toughness to withstand the stress of rapid operations. Conversely, in precision machining, a high-hardness grade might be necessary to ensure that the tool maintains sharpness for precise cuts.
Factors such as cutting speed, feed rate, and the environment in which the tool will operate (e.g., temperature, pressure) also influence the choice of carbide grade.
4. Tool Geometry and Design
Carbide grades can also vary based on the tool geometry and design. For instance, the type of cutting tool (insert, drill bit, or end mill) and its shape will affect which carbide grade is most suitable. For example:
- Carbide inserts: These often come in a variety of grades depending on the application, from general-purpose turning to highly specialized cutting.
- Drill bits: For drilling hard or abrasive materials, a tougher carbide grade may be necessary to prevent chipping of the cutting edge.
Understanding the type of tool and how it will be used is essential in making the right choice.
5. Manufacturer Specifications and Recommendations
When selecting carbide grades, it is always helpful to consider the manufacturer’s recommendations for specific applications. Manufacturers often have detailed specifications for the grades of carbide that work best with their cutting tools, and these can guide you in choosing the right material. You can also review online guides to gain a deeper understanding of how different grades perform in various industrial settings.
6. Cost-Effectiveness
While higher-grade carbide tools typically offer better performance and longer life, they also come at a higher price point. When comparing grades, it’s important to consider the total cost of ownership, which includes not only the upfront cost of the carbide but also the cost of maintenance, downtime, and replacement.
In some cases, a lower-grade carbide tool may offer adequate performance for the intended application, allowing you to save money while still achieving satisfactory results. However, for high-performance or high-precision tasks, investing in a higher-grade carbide tool may prove to be more cost-effective in the long run due to its increased lifespan and performance.
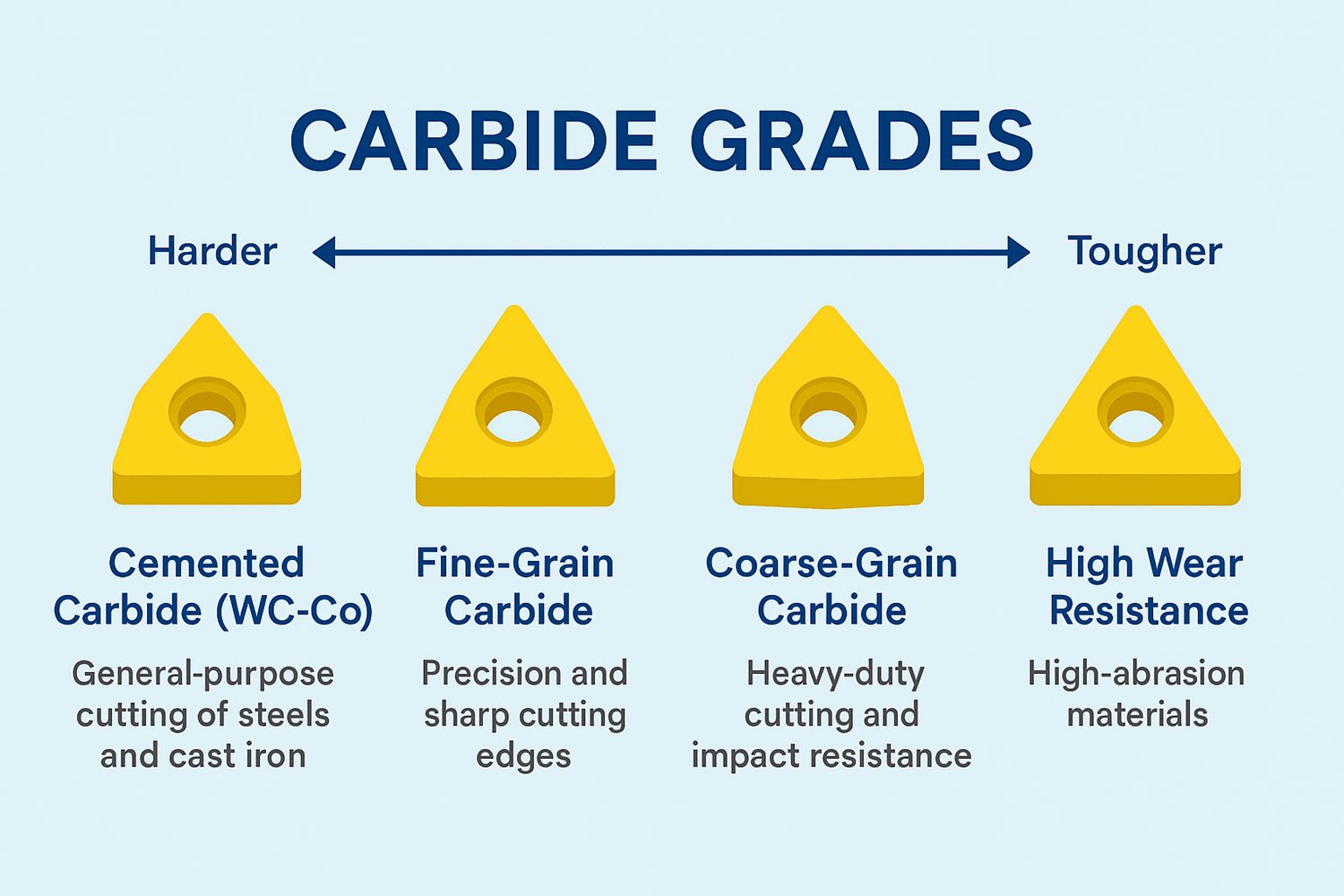
Common Carbide Grades and Their Uses
Here’s an overview of some of the most commonly used carbide grades and their typical applications:
- Cemented Carbide (WC-Co): This is one of the most widely used carbide grades for cutting tools, especially for general machining tasks. It offers a good balance between hardness and toughness and is suitable for materials such as steel, aluminum, and cast iron.
- Fine-Grain Carbide: Ideal for applications requiring precision and sharp cutting edges, fine-grain carbide is often used in applications like high-speed machining and precision tools. It is harder but more brittle, so it’s not ideal for tough or impact-prone materials.
- Coarse-Grain Carbide: Coarse-grain carbide is more tough and resistant to impact, making it suitable for heavy-duty cutting applications such as mining tools, drill bits, and machining rough materials.
- Carbide with High Wear Resistance: For applications involving high-abrasion materials like composites or abrasive metals, this grade is designed for maximum wear resistance and is perfect for cutting tools in demanding environments.
Conclusion
Choosing the right carbide tips and carbide tools is essential for ensuring optimal performance in your industrial operations. By considering factors like material hardness, cutting conditions, tool geometry, and cost-effectiveness, you can select the appropriate carbide grade to meet the specific needs of your application.
Understanding carbide grades and how to compare them ensures that you make informed decisions, resulting in longer tool life, better performance, and cost savings. Always consult with your carbide tool manufacturer or supplier for their recommendations based on your unique requirements.
If you’re looking for high-quality carbide tools, consider exploring trusted suppliers like Leader Hitech for a comprehensive selection of carbide products tailored to your industry needs.